

The fixed distance from the centre to the surface is its radius.Ī net is a flat diagram on one plane that is folded to make a hollow solid. The perpendicular distance from the vertex to the base is the height of the cone.Ī right cone is a cone in which the vertex is vertically above the centre of the base.Ī sphere is a solid in which all points on its curved surface are equidistant from a fixed point which is the centre of the sphere. The length from the vertex to the base is the slant height of the cone. (c) An axis that joins the vertex to the centre of the circular base. (b) A curved surface which meets at a common vertex. The perpendicular distance between the two bases is the height of the cylinder.Ī right cylinder is a cylinder in which the axis is perpendicular to the bases. (c) An axis that joins the centres of two bases at both ends (a) Two parallel opposite faces, called bases, in the shape of congruent circles at both its ends. Pyramids are named after the shapes of their bases. The perpendicular distance from the common vertex to the base is the height of the pyramid.Ī right pyramid is a pyramid in which its vertex is vertically above the centre of the base. The lateral triangular faces meet at a common vertex. Opposite faces have the same shapes and sizes.Ī cube is a special type of cube with edges equal in length. Prisms are named after the shape of their bases.Ī cuboid is a solid with six rectangular faces. It is the same shape and size as its base. The cross section of a prism is the section that is parallel to its base. The perpendicular distance between the two bases is the height of the prism.Ī right prism is a prism in which the bases of the prism are perpendicular to the lateral faces.
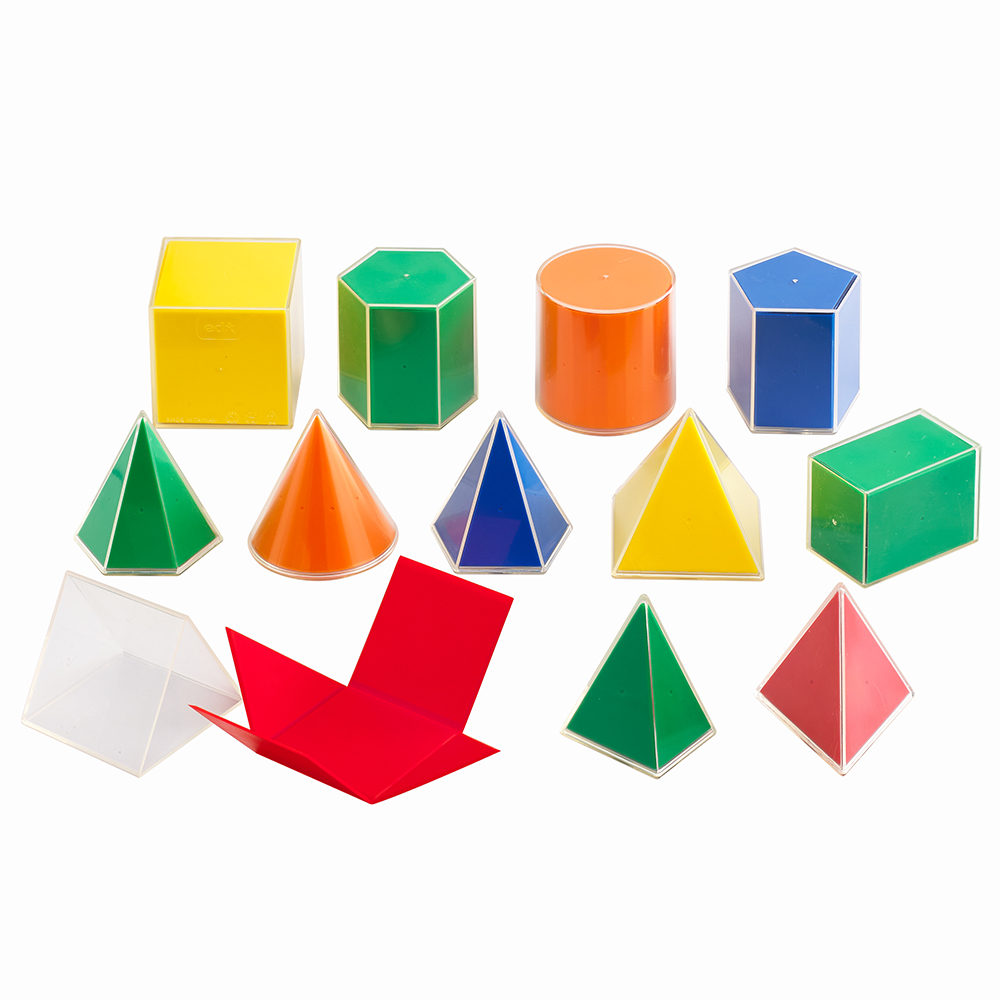
(b) All other faces in the shape of parallelograms are called lateral faces. These congruent polygons are called bases of the prism. (a) Two parallel opposite faces in the shape of congruent polygons. The vertex is the point where three or more edges meet. If a solid has a curved surface, it has no faces. Each surface of a polyhedron is called a face of the solid. A solid with all its surfaces flat is a polyhedron. Every solid has flat surfaces or curved surfaces or both types of surfaces (flat and curved). The face of a solid is a flat or curved surface that is two-dimensional in shape. Geometric solids are three-dimensional figures that have length, breadth and height.Įvery geometric solid has a fixed number of edges, vertices and faces.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
